Cognitive computing is a rapidly evolving field within artificial intelligence (AI) that aims to simulate human thought processes and decision-making. It involves creating computer systems that mimic the way the human brain works, allowing machines to understand, learn from, and interact with the world in a more natural, human-like manner. By integrating various AI technologies, such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and deep learning, cognitive computing systems can analyze complex data, reason, and make informed decisions. In 2024, cognitive computing continues to revolutionize industries, enhancing productivity and reshaping human-computer interactions.
What is Cognitive Computing?
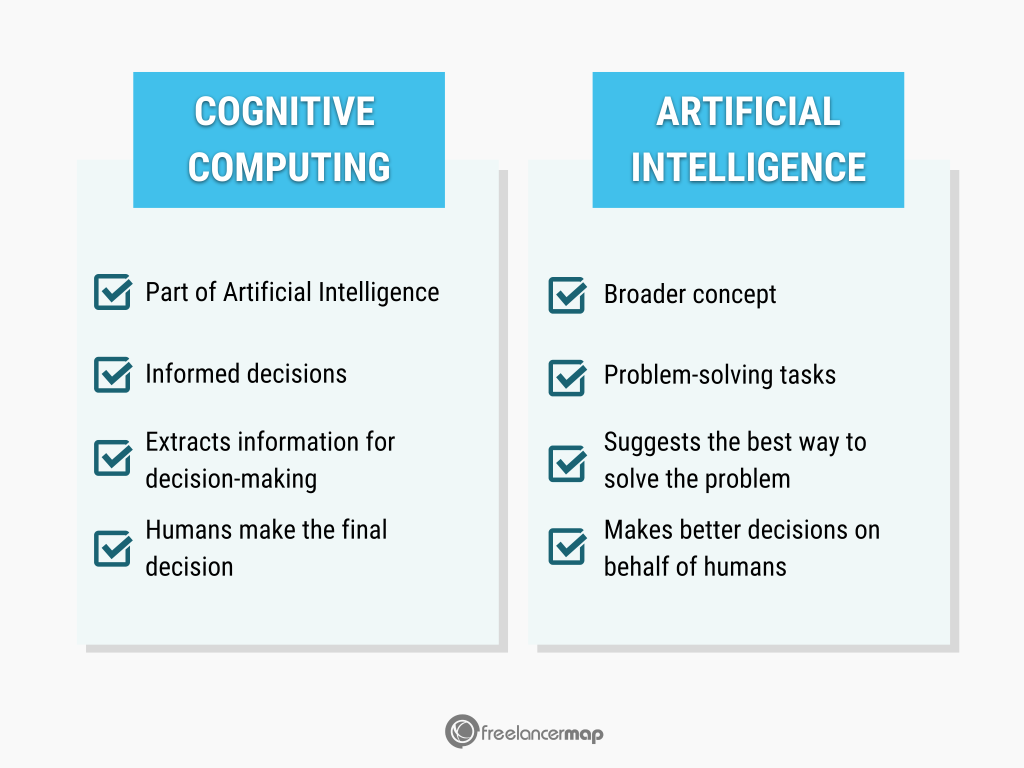
Cognitive computing refers to a technology that aims to emulate human cognitive processes. Unlike traditional computing systems, which are programmed to follow predefined rules and execute specific tasks, cognitive computing systems are designed to understand, reason, learn, and interact in a more human-like way. They utilize advanced algorithms and AI models to process and analyze unstructured data, such as natural language, images, and sounds, allowing them to derive insights, make predictions, and solve complex problems.
The goal of cognitive computing is not to replace human intelligence but to augment it. By enabling machines to think, cognitive computing aims to enhance human decision-making capabilities and assist in tasks that are too complex or time-consuming for people to handle alone. Cognitive systems learn and adapt over time, improving their accuracy and performance based on new information and experiences.
Core Components of Cognitive Computing
Several core components make up cognitive computing systems, each contributing to their ability to mimic human thought processes:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables machines to understand and interpret human language, making it possible for cognitive systems to interact with users in a more intuitive way. Through NLP, cognitive computing systems can analyze text, recognize speech, and generate human-like responses.
- Machine Learning and Deep Learning: These technologies enable cognitive systems to learn from data and improve over time. Machine learning allows systems to identify patterns and make predictions based on historical data, while deep learning uses neural networks to process complex information, such as images or audio, in a similar way to the human brain.
- Reasoning and Inference Engines: Cognitive computing systems use reasoning engines to draw conclusions based on available data. These engines simulate human reasoning by applying logic and rules to derive insights and make decisions. Inference engines help cognitive systems handle ambiguous or incomplete information, similar to how humans use context to understand meaning.
- Computer Vision: This component enables cognitive computing systems to analyze and interpret visual information. By recognizing objects, faces, and patterns in images or videos, cognitive systems can make sense of the visual world in ways that traditional computing cannot.
- Speech Recognition: Speech recognition allows cognitive systems to understand spoken language and convert it into text or actions. This capability is essential for voice-activated assistants and other applications that involve human-machine interaction.
Real-World Applications of Cognitive Computing in 2024
In 2024, cognitive computing is being used across various industries to solve complex problems, enhance productivity, and improve user experiences. Here are some of the most impactful applications:
1. Healthcare
Cognitive computing is transforming healthcare by enhancing the way medical professionals diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. Cognitive systems can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, medical literature, and genetic information, to provide insights into the best treatment options for individual patients.
For example, cognitive computing systems like IBM Watson Health are used to assist doctors in diagnosing complex diseases such as cancer. By analyzing a patient’s medical history and comparing it with extensive medical research, the system can recommend personalized treatment plans that are more effective than standard approaches. Additionally, cognitive computing is being used to predict disease outbreaks, monitor patient health in real-time, and assist in drug discovery by identifying potential candidates more quickly.

2. Finance
In the finance industry, cognitive computing is used to detect fraudulent activities, manage risks, and automate customer service. Cognitive systems analyze transaction patterns to detect anomalies that may indicate fraud, allowing financial institutions to take immediate action to protect their customers.
Risk assessment is another key area where cognitive computing is making an impact. By analyzing historical financial data, market trends, and external factors, cognitive systems can predict potential risks and help financial professionals make informed investment decisions. In customer service, cognitive chatbots equipped with NLP can assist customers by answering queries, processing requests, and even providing financial advice, all while learning from interactions to improve over time.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Cognitive computing is revolutionizing retail and e-commerce by enabling personalized shopping experiences. Cognitive systems can analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing history to recommend products that are most likely to interest individual shoppers. This level of personalization enhances customer satisfaction and increases sales for retailers.
Additionally, cognitive computing is used in inventory management and supply chain optimization. By predicting demand for products, cognitive systems help retailers maintain optimal stock levels, reducing both overstocking and stockouts. This not only improves operational efficiency but also minimizes costs associated with excess inventory.
4. Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, cognitive computing is being used to optimize production processes, ensure quality control, and reduce downtime. Cognitive systems analyze data from sensors in machinery to predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing companies to perform maintenance proactively. This approach, known as predictive maintenance, helps manufacturers avoid costly unplanned downtime and extends the life of their equipment.
Cognitive computing is also used in quality control processes. By analyzing images of products on the assembly line, cognitive systems can detect defects or inconsistencies, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
5. Customer Service and Support
Cognitive computing is enhancing customer service across industries by enabling the development of intelligent virtual assistants and chatbots. These AI-powered systems use NLP and machine learning to understand customer queries, provide relevant responses, and even resolve issues without human intervention. As they interact with more customers, these systems continue to learn and improve, offering more accurate and personalized support over time.
For example, companies like Microsoft and Google are using cognitive computing to power their virtual assistants, such as Cortana and Google Assistant. These assistants can perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions and setting reminders to controlling smart home devices, making them valuable tools for both businesses and individual users.
6. Education
In education, cognitive computing is being used to create personalized learning experiences for students. Cognitive systems can analyze a student’s progress, learning style, and knowledge gaps to provide customized educational content that meets their individual needs. This approach helps students learn more effectively and at their own pace.
Cognitive computing also supports educators by automating administrative tasks such as grading, attendance tracking, and managing student records. This allows teachers to focus more on instruction and less on paperwork, enhancing the overall learning environment.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Cognitive Computing
While cognitive computing offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges and ethical concerns that need to be addressed:
- Privacy and Data Security: Cognitive computing systems often require access to large amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data protection. Ensuring that data is stored and processed securely is essential to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
- Bias in AI Models: Cognitive systems can inherit biases from the data used to train them. If training data contains biases, the system may produce biased outcomes, which can be harmful in decision-making processes. Efforts must be made to identify and mitigate bias in cognitive computing applications.
- Job Displacement: As cognitive computing automates tasks traditionally performed by humans, there is concern about job displacement. While the technology can create new opportunities, it may also render some jobs obsolete, requiring workers to adapt and learn new skills.
The Future of Cognitive Computing
Cognitive computing is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of AI and human interaction. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect more seamless integration of cognitive systems into everyday life, making interactions with machines more natural and intuitive. With continued research and development, cognitive computing will help solve complex problems across industries, from healthcare and finance to education and customer service.





